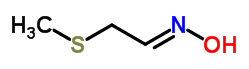
Is methylthioacetaldehyde oxime really an intermediate in the synthesis of methomyl?
Methylthioacetaldehyde oxime is indeed an intermediate in the synthesis of methomyl, which is a widely used insecticide. Methomyl is a carbamate insecticide that works by inhibiting the activity of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase in insects, leading to the accumulation of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and ultimately causing paralysis and death in the targeted pests.
The synthesis of methomyl involves several steps, and methylthioacetaldehyde oxime is one of the key intermediates in this process. Here is a simplified overview of the synthesis:
1. Starting Materials: The synthesis typically starts with the reaction of methyl isocyanate and thioacetamide to form methylthioacetaldehyde oxime.
2. Conversion to Methomyl: Methylthioacetaldehyde oxime is further processed through a series of chemical reactions to eventually yield methomyl. These reactions may involve the introduction of additional functional groups and the formation of the carbamate structure characteristic of methomyl.