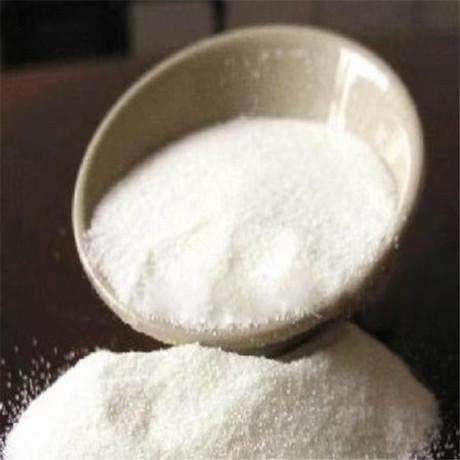
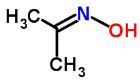
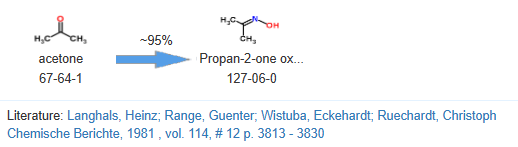
Dimethyl ketoxime, often abbreviated as DMKO, is a chemical compound with the molecular formula (CH3)2C(NOH)C(H)NOH. It is derived from the ketone acetone (propanone) by converting one of its carbonyl (C=O) groups into an oxime (-NOH) group. The term "dimethyl" indicates that there are two methyl groups (-CH3) attached to the nitrogen atom of the oxime group.
Dimethyl ketoxime is commonly used as a chelating agent and as a reagent in analytical chemistry, particularly for the detection and quantification of metal ions. Its oxime functional group has a strong affinity for certain metal ions, such as copper, nickel, and cobalt, forming stable complexes. This property makes DMKO useful in various applications, including:
1. Metal Ion Analysis: DMKO is employed to extract and analyze metal ions from solutions, such as in the determination of metal concentrations in environmental samples or industrial processes.
2. Catalysis: It can be used as a ligand in coordination chemistry and catalysis, where it can help stabilize metal complexes in various reactions.
3. Inhibitor: DMKO is sometimes used as an inhibitor for the corrosion of metals, especially in situations where copper corrosion needs to be controlled.
4. Separation Techniques: DMKO can be used in chromatographic techniques, such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), for the separation and quantification of metal complexes.
5. Coordination Chemistry: It is used in the synthesis of various coordination compounds and metal complexes for research and industrial applications.