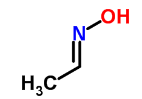
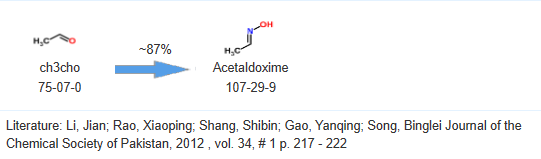
Acetaldehyde oxime, also known as ethanal oxime or oximoethane, is a chemical compound with the molecular formula
C2H5NO. It is derived from acetaldehyde (ethanal) by replacing the carbonyl group (C=O) with an oxime group (-C=N-OH). The chemical structure of acetaldehyde oxime can be represented as follows:
CH3CHO + H2N-OH → CH3C(NOH)H2
Acetaldehyde oxime is used in organic synthesis as a reagent and can be involved in various chemical reactions to produce different compounds. Its primary use is in the formation of oxime ethers or hydrazones through condensation reactions. These derivatives can serve as intermediates in the synthesis of various organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
Additionally, acetaldehyde oxime can be used as a chelating agent in analytical chemistry and as a stabilizer for certain polymers. It has a variety of other potential applications in organic chemistry and chemical processes, depending on the specific reaction and desired products.